
Historically, manufacturing in the United States has played a vital role in supporting the nation's economy and jobs. It is important that the United States, while still the third largest manufacturer in the world remains heavily dependent on other countries for most of its production needs. The United States now faces many challenges, including a dearth of manufacturing capacity, and a highly competitive manufacturing environment. In order to strengthen our economy and address these challenges, the United States needs to strengthen its innovation system.
The highest wages in America are also earned in manufacturing. The United States' largest economic contributor is its manufacturing sector, which accounts for more than 12 % of gross domestic product (GDP), as well as about 6 percent of all jobs. Manufacturing is not dying, as many assume.

Technology has played an important role in the manufacturing industry in the United States, and in the last several years, there has been a flurry of new production technology that has enabled companies to produce more efficiently and faster. The technology allows for lower costs through more efficient processes. American manufacturers will be more competitive by increasing the efficiency of production.
Technology in other areas has also helped the manufacturing industry. Automation has made manufacturing more efficient, which helps keep costs down.
Maintaining manufacturing in the United States is crucial for the security of our financial system. Consumers are increasingly conscious of environmental standards and value companies that manufacture their goods in the United States. Companies that invest in their local communities and help them hire their people are valued by many customers.
Another reason why the United States should continue manufacturing is because it is more sustainable. The United States has a lower energy consumption than other countries' manufacturing industries. This has many advantages, including a reduced carbon footprint and the ability of goods being shipped to customers more efficiently. Keeping manufacturing in the United States also helps to keep costs down in other areas, such as logistics and shipping. The United States' manufacturing sector can lower shipping costs and increase customer satisfaction.
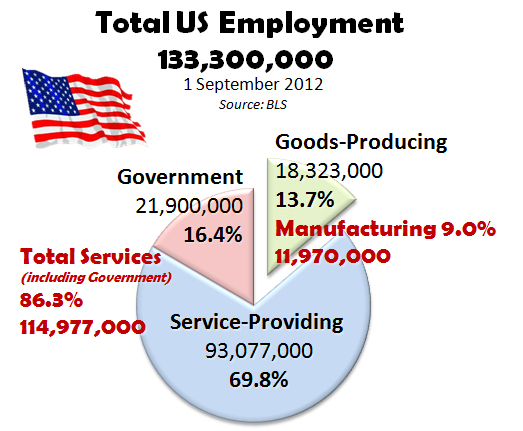
Finally, manufacturing in the United States is a great way to support American workers who are not located on the coasts. Many people have been affected in this country by the recession. This has also led a rise in interest in the U.S. market and a shift in production capabilities. More than 22,000 jobs were created in manufacturing in the United States in the last year. In the coming years, it will be a priority to add jobs to the American economic.
FAQ
What types of jobs can you find in logistics
There are many kinds of jobs available within logistics. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers - They load and unload trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers - They drive trucks and trailers to deliver goods and carry out pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers - They sort and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers – These people oversee inventory at warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents - They purchase goods and services needed for company operations.
-
Customer service representatives - Answer calls and email from customers.
-
Shipping clerks: They process shipping requests and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - They fill orders based on what is ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors - They check incoming and outgoing products for defects.
-
Others - There are many other types of jobs available in logistics, such as transportation supervisors, cargo specialists, etc.
What does "warehouse" mean?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be either an indoor or outdoor space. It may also be an indoor space or an outdoor area.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The difference between a product planner and project manager is that a planer is typically the one who organizes and plans the entire project. A production planner, however, is mostly involved in the planning stages.
What is the job of a logistics manger?
A logistics manager ensures that all goods are delivered on time and without damage. This is accomplished by using the experience and knowledge gained from working with company products. He/she should make sure that enough stock is on hand to meet the demands.
Statistics
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Six Sigma in Manufacturing
Six Sigma refers to "the application and control of statistical processes (SPC) techniques in order to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department in Tokyo, Japan developed Six Sigma in 1986. Six Sigma is a method to improve quality through standardization and elimination of defects. Since there are no perfect products, or services, this approach has been adopted by many companies over the years. Six Sigma aims to reduce variation in the production's mean value. This means that you can take a sample from your product and then compare its performance to the average to find out how often the process differs from the norm. If you notice a large deviation, then it is time to fix it.
The first step toward implementing Six Sigma is understanding how variability works in your business. Once you understand this, you can then identify the causes of variation. It is important to identify whether the variations are random or systemic. Random variations are caused when people make mistakes. While systematic variations are caused outside of the process, they can occur. Random variations would include, for example, the failure of some widgets to fall from the assembly line. If however, you notice that each time you assemble a widget it falls apart in exactly the same spot, that is a problem.
Once you've identified where the problems lie, you'll want to design solutions to eliminate those problems. This could mean changing your approach or redesigning the entire process. After implementing the new changes, you should test them again to see if they worked. If they don't work, you will need to go back to the drawing boards and create a new plan.