The education and training needed for a manufacturing engineer job vary from degree to degree. A master's degree program may be offered to graduates who have the required knowledge in business, product and process. Majority of manufacturing engineers get their majority of their training in their degree program. They get hands-on experience with measurements, experiments and standard tests. Employers will require them to obtain a license in order to operate a business.
Manufacturing engineer skills
Depending on the position, manufacturing engineers can move up from an entry-level position to a management role. Their job description will include the skills they will need to be successful. They should be well-versed in various disciplines, including math and critical thinking. To work with all levels of an organisation, they should have great communication skills. These are just a few skills that manufacturing engineers need to excel in their roles.
The primary duties of a manufacturing engineer include the development, maintenance, or modification of various processes or systems. They are also responsible for assessing the environmental impact of manufacturing processes. They must be analytical thinkers and designers with a thorough knowledge of manufacturing processes. A manufacturing engineer must keep current with current trends and regulations, as well as stay on top of industry news. They must also be able and willing to collaborate with engineers from different disciplines.
Responsibilities as a Manufacturing Engineer
Manufacturing engineers are responsible for developing and determining production costs. These engineers are responsible for the design and development of production processes. While they often work in an office setting, they may have to travel to other areas such as the factory floor. Some manufacturing engineers might need to oversee or direct production personnel. They are responsible for the smooth operation of a production line.
As a manufacturing engineer, your main responsibility is to develop and implement manufacturing processes. You also need to monitor their efficiency. Manufacturing engineers are responsible for analyzing production processes and designing equipment. They also create quality control systems to ensure that products meet the highest quality standards. Apart from designing and developing manufacturing process, they must also comply with safety and regulatory standards. A manufacturing engineer's duties extend beyond their workplace. They must also conduct research and create reports and documentation.
For manufacturing engineers, the future looks bright
Manufacturing engineers have an excellent career outlook. Compared to other occupations, their growth is slower, though job creation is expected to be higher than average. Manufacturing engineers will be more employed as a result. Manufacturing companies are dependent on the ability to plan and implement logistics. Despite slow growth there is a high demand for mechanical engineering. Most job seekers will come from the school system.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics the U.S. population will have a greater number of manufacturing engineers by 2026. These professionals require teamwork and a demanding work environment. Manufacturing engineers are highly satisfied with their careers and stay in the industry for long periods of time. Manufacturing engineers might work in factories that produce cars and trucks. There are also opportunities for manufacturing engineers to work in consulting, research and-development firms, or wholesale trading. Many industrial engineers choose to leave engineering to become managers.

Manufacturing engineers need to be educated
An undergraduate degree in engineering (BSE) is typically required for most manufacturing engineer jobs. Students will be able to learn about general science, math and engineering concepts. They can also use computer-aided design software (CAD). Students will also be expected to have strong communication skills as well as a solid mathematical foundation. Courses in ethics and humanities may also be required. While education requirements for manufacturing engineers are not uniform, BSEs are considered well-rounded.
The education requirements for a career in manufacturing engineering require strong mathematics and science backgrounds, as well as analytical and problem-solving skills. A team-working skill is essential as well as creativity. After graduating, most manufacturing engineers work full time. Manufacturing engineers are expected to travel extensively and observe various manufacturing processes at different locations. Manufacturing engineers must not only have the right education, but also have a strong work ethic. They should also be eager to learn about the latest trends and manufacturing.
FAQ
What are my options for learning more about manufacturing
The best way to learn about manufacturing is through hands-on experience. However, if that's not possible, you can always read books or watch educational videos.
How can efficiency in manufacturing be improved?
First, we need to identify which factors are most critical in affecting production times. Next, we must find ways to improve those factors. If you aren't sure where to begin, think about the factors that have the greatest impact on production time. Once you've identified them all, find solutions to each one.
What is manufacturing and logistics?
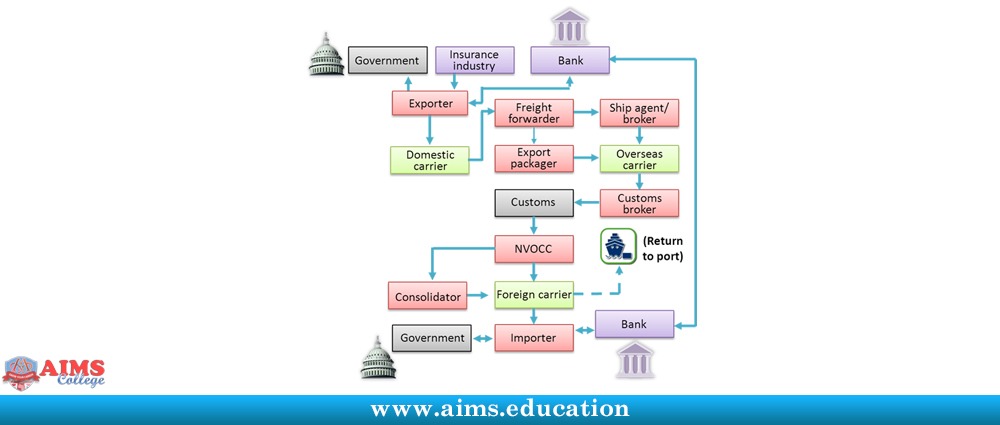
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. Manufacturing and logistics are often considered together as a broader term that encompasses both the process of creating products and delivering them to customers.
What do you mean by warehouse?
A warehouse, or storage facility, is where goods are stored prior to being sold. It can be an indoor space or an outdoor area. In some cases, it may be a combination of both.
What is the responsibility for a logistics manager
A logistics manager ensures that all goods are delivered on time and without damage. This is done by using his/her experience and knowledge of the company's products. He/she must also ensure sufficient stock to meet the demand.
What is the difference between Production Planning and Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP) is the process of determining what needs to be produced at any given point in time. This can be done by forecasting demand and identifying production capabilities.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
What does it take to run a logistics business?
A successful logistics business requires a lot more than just knowledge. To communicate effectively with clients and suppliers, you must be able to communicate well. You will need to know how to interpret data and draw conclusions. You must be able and able to handle stress situations and work under pressure. To improve efficiency, you must be innovative and creative. Strong leadership qualities are essential to motivate your team and help them achieve their organizational goals.
You must be organized to meet tight deadlines.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
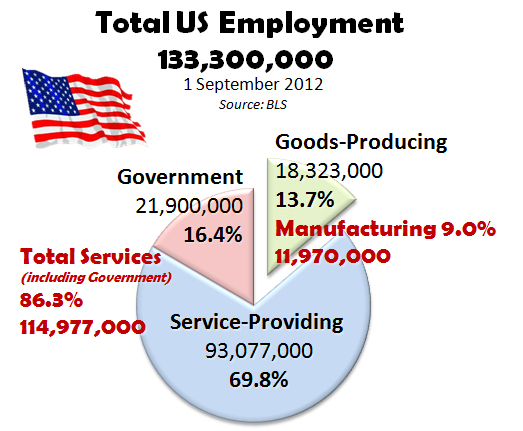
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was developed in Japan during the 1970s and 1980s by Taiichi Ohno, who received the Toyota Production System (TPS) award from TPS founder Kanji Toyoda. Michael L. Watkins published the original book on lean manufacturing, "The Machine That Changed the World," in 1990.
Lean manufacturing is often defined as a set of principles used to improve the quality, speed, and cost of products and services. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean manufacturing has been deemed one of the best ways to manage the entire value-chain, including customers, distributors as well retailers and employees. Lean manufacturing is widely used in many industries. Toyota's philosophy, for example, is what has enabled it to be successful in electronics, automobiles, medical devices, healthcare and chemical engineering as well as paper and food.
Five basic principles of Lean Manufacturing are included in lean manufacturing
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Eliminate any activity that doesn't add value along the supply chain.
-
Create Flow - Make sure work runs smoothly without interruptions.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Build Relationships - Establish personal relationships with both internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing is not a new concept, but it has been gaining popularity over the last few years due to a renewed interest in the economy following the global financial crisis of 2008. To increase their competitiveness, many businesses have turned to lean manufacturing. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing, which has many benefits, is now a standard practice in the automotive industry. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT stands for a system where components are assembled on the spot rather than being made in advance. This approach is designed to reduce lead times and increase the availability of components. It also reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM): ZDM focuses on ensuring that no defective units leave the manufacturing facility. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished products, which may need minor repairs before they are shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous Improvement aims to improve efficiency by continually identifying problems and making adjustments to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous Improvement involves continuous improvement of processes.