
Manufacturing engineers must convert raw materials and create new, updated products. They are also responsible for creating systems that integrate the production process and supervising those who are involved in its manufacture. This career can be rewarding, with a high level of job satisfaction and a good work-life balance.
In the US, a manufacturing engineering salary averages $77.500 per year. This figure was derived from data collected by 655 TurboTax customers who identified themselves as manufacturing engineers. It includes taxable wages and bonuses.
What is Manufacturing Engineering Salary?
The manufacturing engineering salary varies from $28,500 to a maximum of $178.500. This depends on the education level, skills, experiences, employer & geographical location. Those with experience tend to earn higher salaries than those who do not.

Salary of Entry-Level Manufacturing Engineer: The average salary for a manufacturing engineer at the entry-level is $52,000. The average entry-level manufacturing engineer salary can vary by state.
In general, you will need to have a Bachelor's Degree in a relevant discipline. This can be in any one of the many engineering specialties or a more general subject such as computer science or electrical engineering. However, it's best to have a graduate degree if you want to advance in the field or conduct research.
What is a typical manufacturing engineering job?
Engineers are often responsible for designing and developing systems that increase productivity at work. These engineers are experts in creating processes that transform raw materials into finished goods, while focusing on reducing waste. These engineers also have a great deal of problem-solving skills that allow them to quickly identify and solve problems in the process of developing new products or upgrading existing ones.
What do manufacturing engineers do on a daily basis?
A manufacturing engineer's main duties include maintaining projects on schedule and within budget, as well as ensuring production efficiency and high quality. It is important that they are able to communicate well with design engineers as well as technicians and management. They also need to understand the impact of their decisions on production costs and timelines and how they can manage these factors for the benefit of all project members.
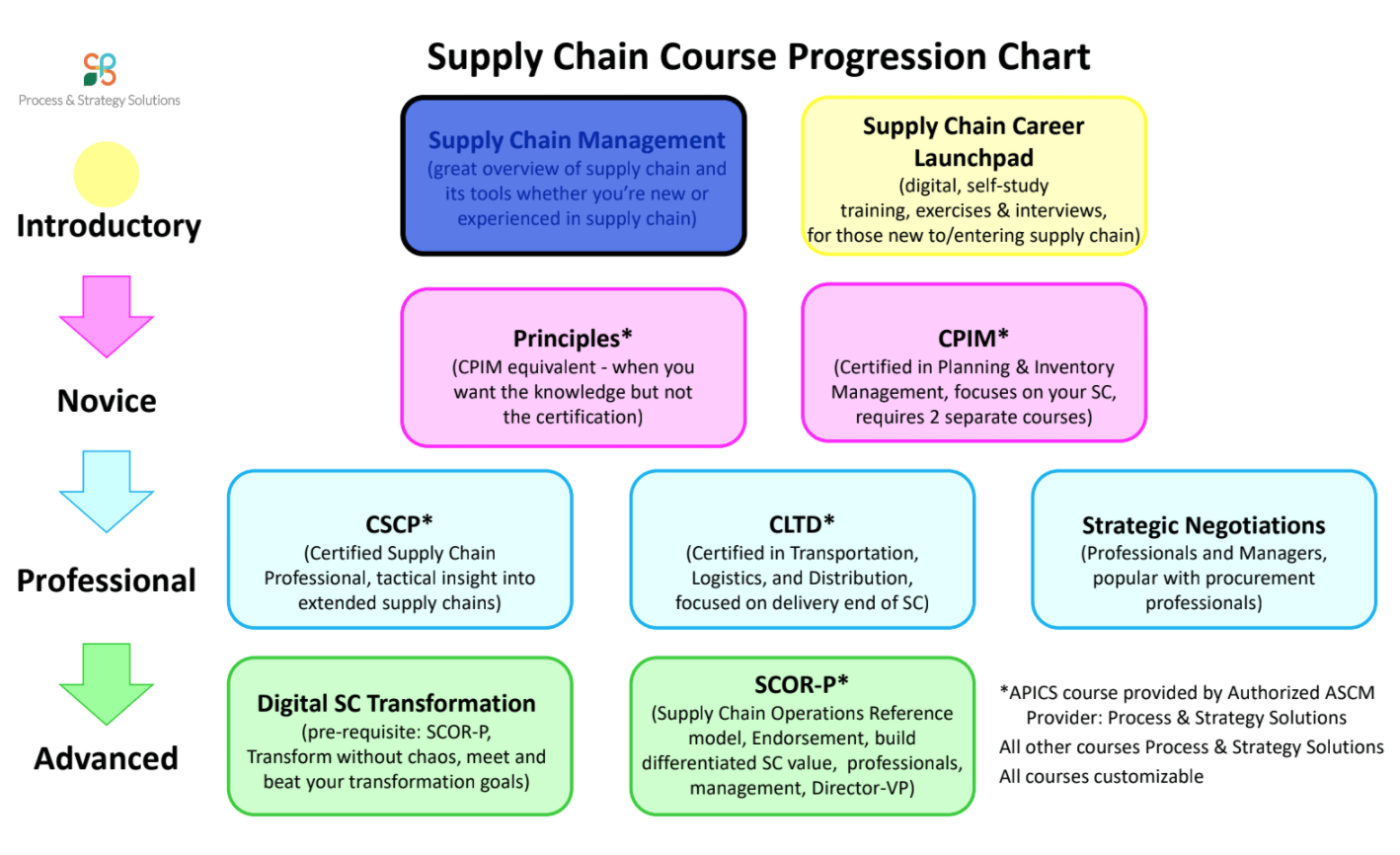
What qualifications are required to become an industrial and manufacturing engineer?
Manufacturing engineers are required by most companies with their own production. These can include large multinational corporations, small companies, research and development labs or local companies that produce a wide variety of products, from pharmaceuticals to food and drink.
What are the most common jobs for manufacturing engineers in the United States?
Manufacturing engineers are employed in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, defence, software and hardware, robotics, and assembly line automation. Manufacturing engineers may work from an office, a lab or a factory.
What is the average manufacturing engineers salary?
The manufacturing engineer salary ranges from $57,839 to $86,809 annually in the US. This figure is calculated using data from TurboTax Users who have reported their occupation of manufacturing engineer. It includes tips, bonuses, taxable wage, and more.
FAQ
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP), is the process of deciding what production needs to take place at any given time. This is accomplished by forecasting the demand and identifying production resources.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
How important is automation in manufacturing?
Automating is not just important for manufacturers, but also for service providers. It allows them to offer services faster and more efficiently. In addition, it helps them reduce costs by reducing human errors and improving productivity.
What are the responsibilities of a logistic manager?
Logistics managers make sure all goods are delivered on schedule and without damage. This is accomplished by using the experience and knowledge gained from working with company products. He/she also needs to ensure adequate stock to meet demand.
How can we improve manufacturing efficiency?
First, identify the factors that affect production time. The next step is to identify the most important factors that affect production time. You can start by identifying the most important factors that impact production time. Once you have identified the factors, then try to find solutions.
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing refers to the transformation of raw materials into useful products by using machines and processes. It can involve many activities like designing, manufacturing, testing packaging, shipping, selling and servicing.
What does warehouse mean?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be an outdoor or indoor area. In some cases it could be both indoors and outdoors.
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just-In-Time Method in Production
Just-in-time (JIT) is a method that is used to reduce costs and maximize efficiency in business processes. This is where you have the right resources at the right time. This means you only pay what you use. Frederick Taylor, a 1900s foreman, first coined the term. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He then concluded that if he could ensure that workers had enough time to do their job before starting to work, this would improve productivity.
The idea behind JIT is that you should plan ahead and have everything ready so you don't waste money. It is important to look at your entire project from beginning to end and ensure that you have enough resources to handle any issues that may arise. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven JIT: This is a JIT that allows you to regularly order the parts/materials necessary for your project. This will allow you to track how much material you have left over after using it. It will also allow you to predict how long it takes to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This type allows you to stock the materials needed for your projects ahead of time. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This approach involves setting aside sufficient funds to cover your project's costs. When you know how much you need, you'll purchase the appropriate amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT is the most widespread form. You assign certain resources based off demand. For example, if there is a lot of work coming in, you will have more people assigned to them. If you don't receive many orders, then you'll assign fewer employees to handle the load.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based: This approach is very similar to the cost-based method except that you don't look at individual workers costs but the total cost of the company.
-
Material-based is an alternative to cost-based. Instead of looking at the total cost in the company, this method focuses on the average amount of raw materials that you consume.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each employee, you will focus on the time it takes to complete a project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about the costs of each employee or how long it takes for something to be made, you should think about how quality your product is.
-
Value-based: This is one of the newest forms of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based. This method is inventory-based and focuses only on the actual production at any given point. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-in-time (JIT) planning: This is a combination of JIT and supply chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. It is essential because it reduces lead-times and increases throughput.